Ls-Opt
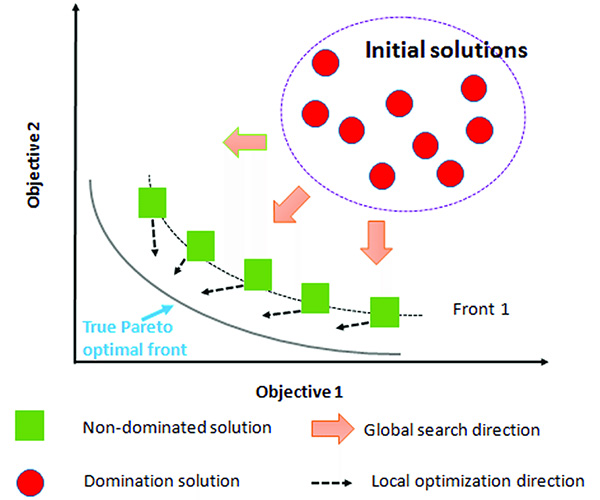
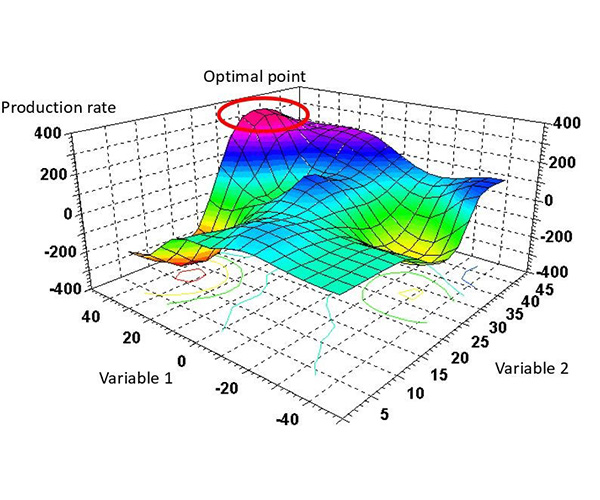
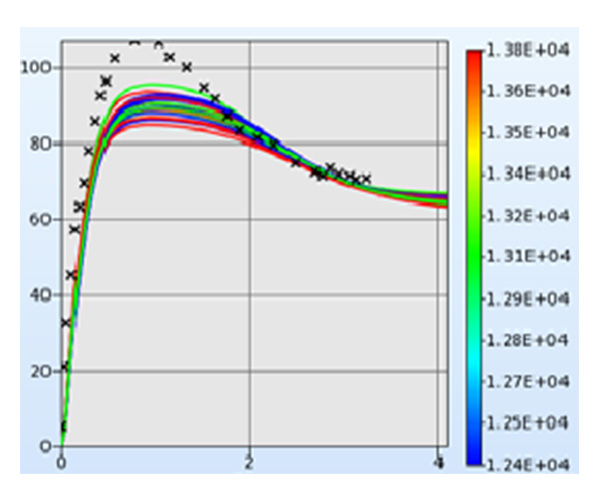
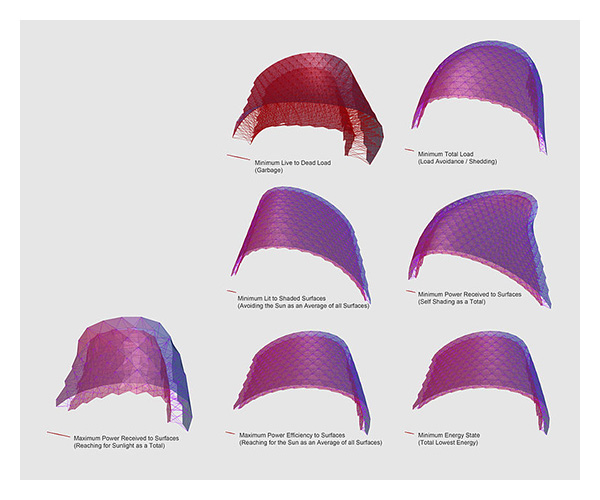
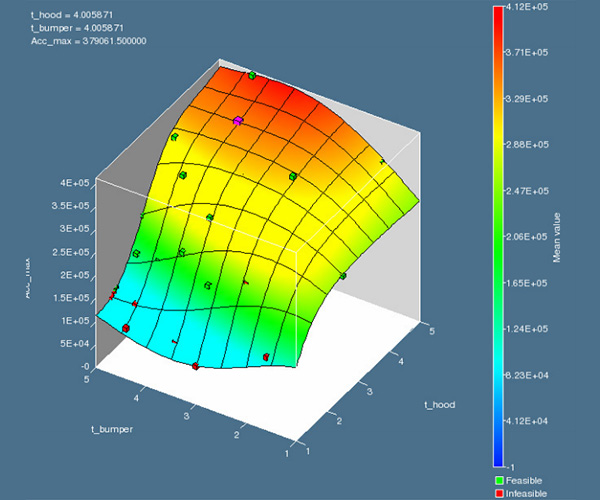
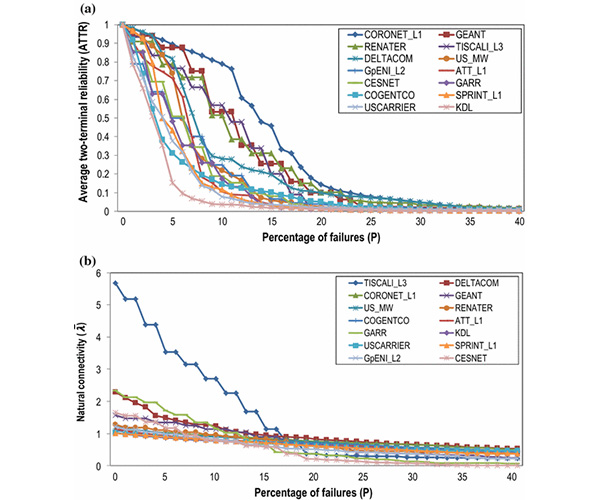
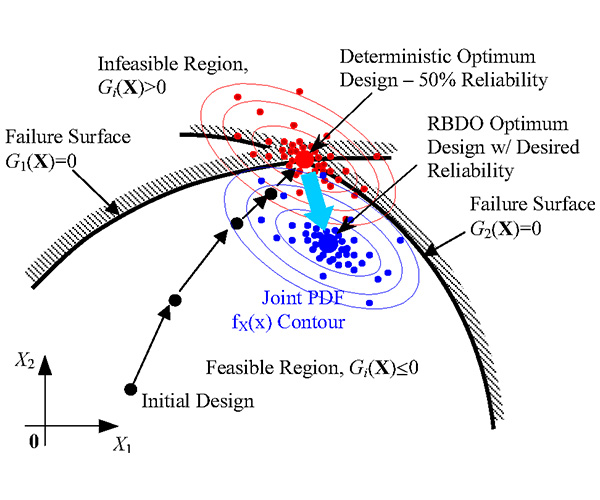
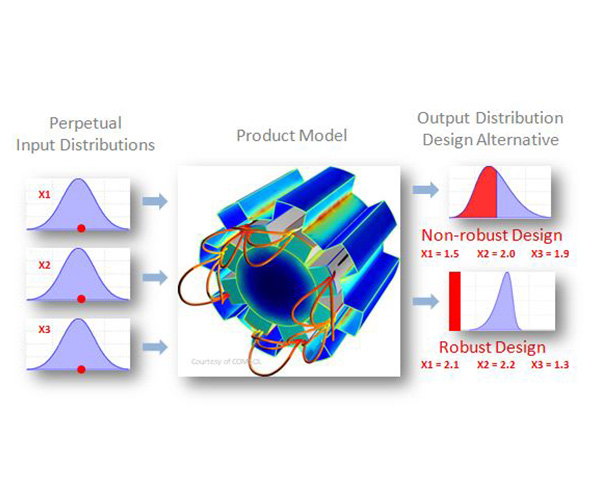
LS-OPT is an optimization tool which interfaces perfectly with LS-DYNA, allowing the user to structure the design process, explore the design space and compute optimal designs according to specified constrains and objectives. It is highly suitable for solving system identification problems and stochastic analysis.
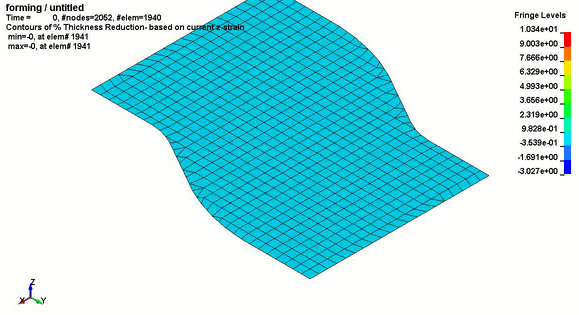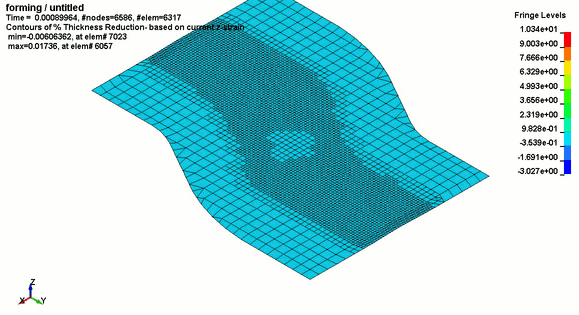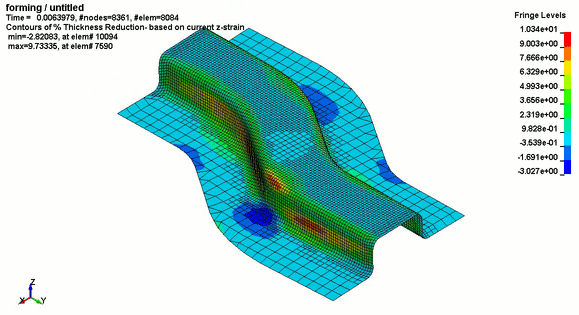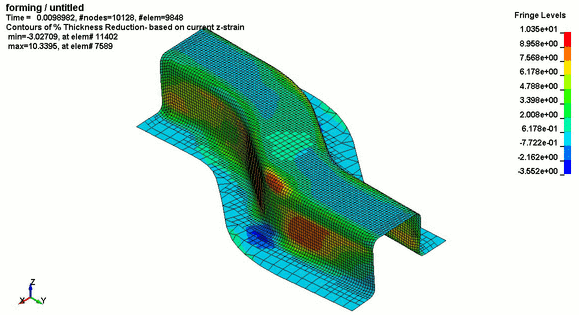


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
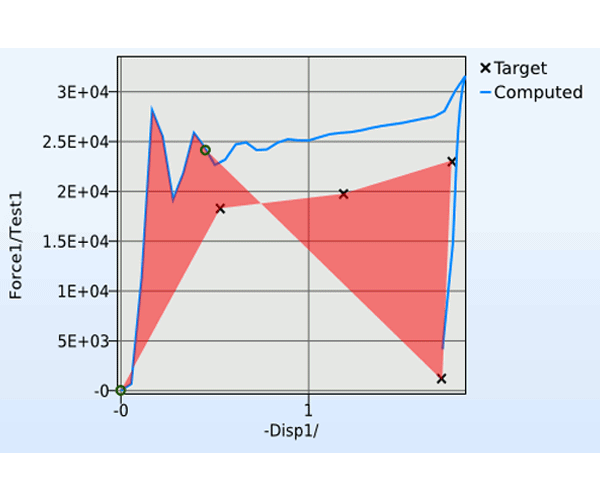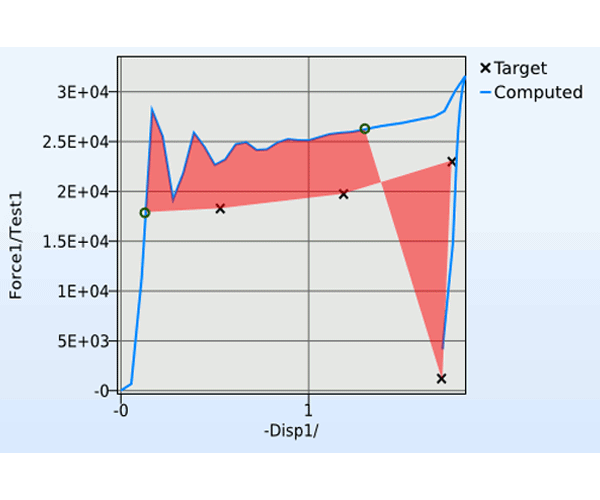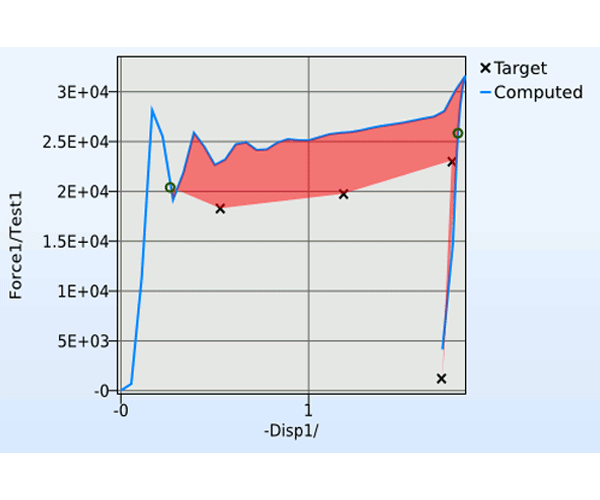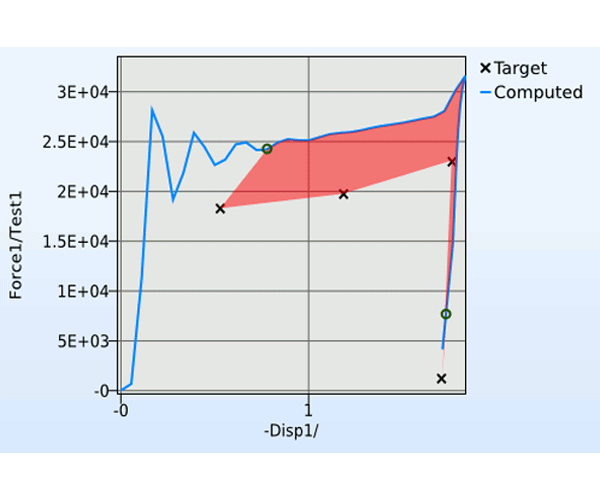
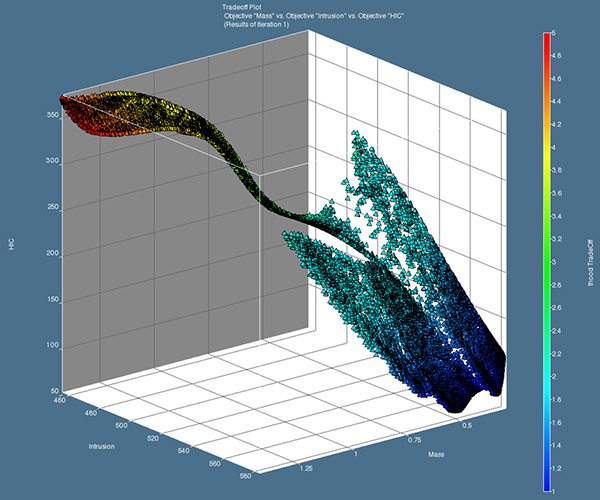
.jpg)
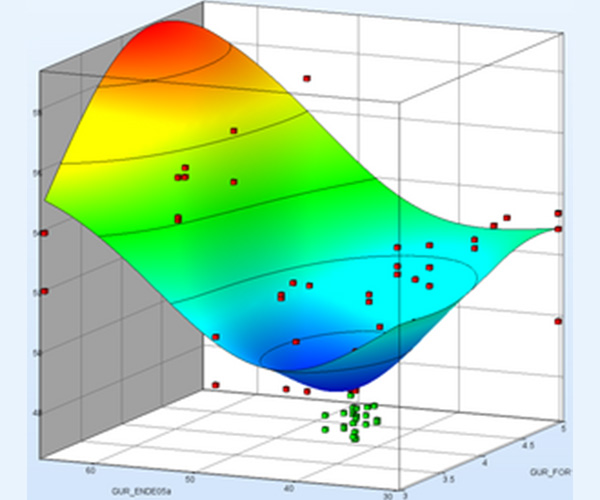
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
